Describe the Structure of the Bone
21 rows Gross Anatomy of Bones. The periosteum plays a crucial role in bone growth and repair.

Pin By Abhijit Kunde On Health And Fitness Human Anatomy Human Respiratory System Human Body Systems
Composition of bone 13 organic collagen fiber matrix 88 organized around lamellae non-collagen 12.

. Describe the microscopic structure of compact bone. Start your trial now. The bones get their strength from storing minerals eg.
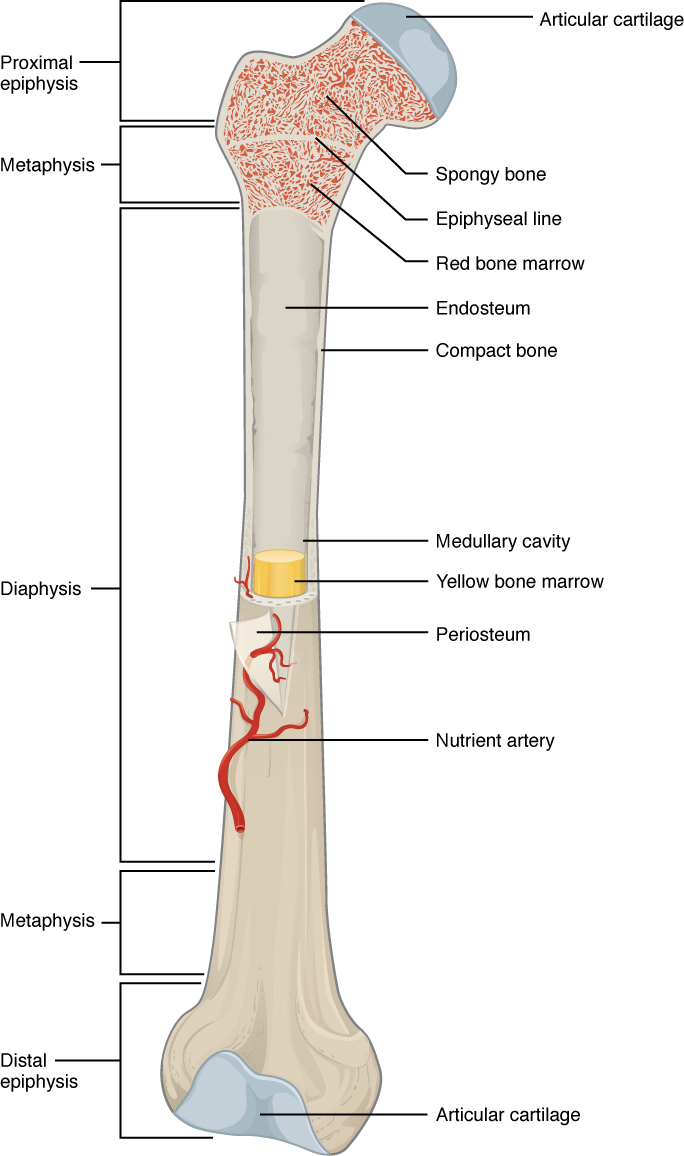
A typical long bone shows the gross anatomical characteristics of bone. Describe the microscopic structure of bone. Bone tissue osseous tissue differs greatly from other tissues in the body.
Here we explain the anatomy of bone and the function of each part. Of its dry mass approximately 60-70 is bone mineral. These canals called Haversian canals are.
STUDY PLAY Diaphysis growing between Is the bones shaft or body---the long cylindrical main portion of the bone. First week only 499. There are two types of bone tissue.
The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone Figure 1. Cortical bone Substantia compacta. There are three types of cells that contribute to bone homeostasis.
Compact bone tissue is composed of osteons and forms the external layer of all bones. The diaphysis and the epiphysis. It is also the method of depositing new tissue on the bone surface even past.
Describe how bones are nourished and innervated. Bones are a living tissue which is muscular and firm. The ends of a long bone contain spongy bone and an epiphyseal line.
A long bone has two main regions. Structure of Bone Describe the parts of a long bone and the histological features of bone tissue. 28hermizan halihanafiah histology of bone tissuehistology of bone tissue examine the structure of bone at microscopic levelexamine the structure of bone at microscopic level.
Check out a sample QA here. Describe the microscopic structure of bone. Spongy bone tissue is composed of trabeculae and forms the inner part of all bones.
The structure of a long bone allows for the best visualization of all of the parts of a bone. In vivo bone living bone in the body contains between 10 and 20 water. It also plays an important role in thickening strengthening and remodeling of the long bones.
Despite its inert appearance bone is a highly dynamic organ that is continuously resorbed by osteoclasts and neoformed by osteoblasts. The diaphysis is the tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. Table 62 describes the bone markings which are illustrated in Figure 610.
The bones that are produced by intramembranous ossification are the flat bones of the skull and most of the clavicle. Spongy bone also known as cancellous bone or trabecular bone is a very porous type of bone. Bone is a modified form of connective tissue which is made of extracellular matrix cells and fibers.
The most robust aspect of this unit is the underlying bony architecture. Bone or osseous tissue contains abundantbone or osseous tissue contains abundant extracellular matrix which surrounds widelyextracellular matrix which surrounds. Long bones have a thick outside layer of compact bone and an inner medullary cavity containing bone marrow.
These include the periosteum compact bone spongy bone and an inner core of bone marrow. Textus osseous compactus. This essential membrane is attached to bones by strong collagenous fibers called Sharpeys fibres.
Osteocytes osteoclasts osteoprogenitor cells and osteoblasts. Want to see the step-by-step answer. Glycoproteins proteoglycans lipids etc 13 inorganic mineral mostly dense calcium phosphate in the form of highly insoluble crystals of hydroxyapatite 13 water cells osteoblasts osteoclasts osteocytes bone lining.
Explain membrane bone formation be sure to include types of bones that form this way. Clavicle and Scapula Humerus Radius and Ulna Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges and Sesamoid Two Pelvis bones Femur Tibia Patella and the Fibula Tarsals and Metatarsals Bone Type Explanation Of Bone Example Of Bone Long Bones It is hard Dense They provide the strength structure and movement for the body. Epiphyses growing over Are the distal and proximal ends of the bone.
It is important for bones to. There are three general classes of bone markings. Structure of Bone Tissue.
A long bone has a shaft and 2 ends. Bone itself consists mainly of collagen fibres and an inorganic bone mineral in the form of small crystals. The strength shape and stability of the human body are dependent on the musculoskeletal system.
1 articulations 2 projections and 3 holes. The epiphyseal line is a remnant of an area that contained hyaline cartilage that grew during childhood to lengthen the bone. A long bone has two parts.
Osteoblasts are bone-forming cell osteoclasts resorb or break down bone and osteocytes are mature bone cells. The ground substance of bone is arranged in concentrated layers lamellae round the small canals which run parallel to the long axis shaft of the bone. Bone exerts important functions in the body such as locomotion support and protection of soft tissues calcium and phosphate storage and harboring of bone marrow 3 4.
Structure of human bones explained Periosteum You can think of the periosteum as a thin double-layered skin or membrane that covers the surface of all bones. Bone is hard and many of its functions depend on that characteristic hardness. Spongy bone is usually located at the ends of the long bones the epiphyses with the harder compact bone surrounding it.
Your bones allow you. They produce blood cells which help the body fight against infections. The names imply that the two types differ in density or how tightly the tissue is packed together.
Slightly to resist breaking. Four types of cells compose bony tissue. A long bone has two parts.
Musculoskeletal System Musculoskeletal System Learning Outcomes Learning Outcomes Identify describe and state the functions Identify describe and state the functions and structure of the musculoskeletal system and structure of the musculoskeletal system Describe the ageing process embryo to Describe the ageing process embryo to senior and gender differences. Find step-by-step Anatomy and physiology solutions and your answer to the following textbook question. The diaphysis and the epiphysis.
As the name implies an articulation is where two bone surfaces come together articulus joint. Compact bone also known as cortical bone is a denser material used to create much of the hard structure of the skeleton. Bone Structure Bone structure consists of a number of layers.

Skeletal System 1 The Anatomy And Physiology Of Bones Nursing Times

Diagram Of Human Bone Anatomy Human Bones Anatomy Human Bones Human Anatomy And Physiology
No comments for "Describe the Structure of the Bone"
Post a Comment